Written by John Wakefield – Owner of Artistry in Glass
Argon-filled double-pane windows (combined with Low-E glass) have become the most popular and cost-effective way to improve the energy efficiency of residential glazing since the 1990s.
But, what is the science behind argon-filling? How does it improve the energy efficiency of your windows? This post explains why argon is effective as a substitute for air in double-pane windows.
The bottom line
If in doubt – purchase argon-filled double-pane windows with low-E glass
Argon-filled double-pane windows with Low-E glass are the best choice for replacement windows in nearly all US climatic zones and residential situations in 2023. The technology is mature and reliable, and high-quality windows will retain their argon at effective levels for 20-25 years.

But remember they may not “pay for themselves”
It’s important to understand that, even though getting new windows will eventually save you money on energy bills, it takes such a long time for the savings to add up that it’s almost like a wash. Check out this post for a detailed breakdown of costs and benefits.
So, just a heads up, don’t fall for window salespeople who promise big savings right away on your utility bills. But at the same time, remember there are plenty of other perks to getting new windows, like better security, less noise, cozier indoor vibes, no more drafts, a more attractive look, safety from lead paint, and the satisfaction of doing your part to reduce CO2 emissions and help the planet.
Understanding Argon-Filled Windows
This post will explain the science and engineering behind argon-filling in double-pane windows. Read on if you are interested – Otherwise:
Jump to this section for Frequently Asked Questions
What is Argon?
Argon is a noble gas that is colorless, odorless, and non-toxic. It is denser than air and is commonly used in industrial applications like welding, lighting, and electronics. In the context of windows, argon gas is used to fill the space between the two panes of a double-pane window.
The Role of Argon in Double-Pane Windows
Argon gas is an excellent insulator, which is why it is used in double-pane windows. When the space between the two panes of glass is filled with argon, it reduces the transfer of heat and cold (by conduction & convection) through the window, making it more energy-efficient. The gas also helps to reduce outside noise and prevents the buildup of frost on the inside of the window during winter months.
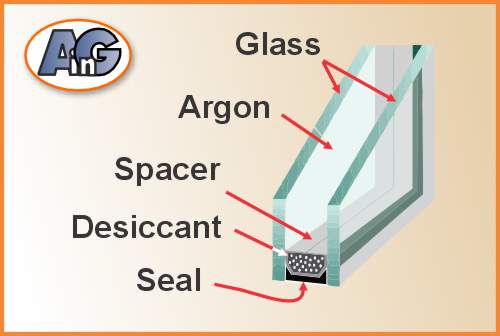
Argon gas is a popular choice for window insulation because it is readily available and inexpensive. It is also non-reactive, which means it does not corrode the materials used in the window, ensuring that the window lasts longer.
However, it is important to note that argon gas is not a magic solution for window insulation. The effectiveness of argon-filled windows depends on several factors, including the quality of the window frame, the glass type, and the installation process. Additionally, argon gas is not a replacement for Low-E coatings, which further improves the energy efficiency of windows.
In summary, argon-filled windows are an excellent choice for homeowners looking to improve the energy efficiency of their homes but the smart homeowner should study the window labels to decide on the best specifications for their climate zone.
To fully understand the EnergyStar labels on your windows – study “Understanding the Labels on Your Double-Pane Glass Windows” – a comprehensive guide from Artistry in Glass.

(Note that Krypton and Xenon are even better insulators but their higher cost makes them less commonly used than Argon).
How exactly does argon cut heat transfer through windows?
Heat is lost (or gained) through windows by three mechanisms radiation, conduction, and convection.
Radiated heat
Radiated heat (infra-red radiation) is not affected by argon filling – in replacement window technology it is controlled by Low-E coatings – described fully in this post

The function of Argon is to reduce conducted and convected heat as described below.
Conducted heat
In any material, heat energy travels from warmer areas to cooler ones through a process called conduction. How fast it goes depends on two things: the temperature difference and how well the materials (glass, gas, and frame) involved can pass heat.
The direction of heat conduction depends on where you live. In chilly northern winters, the goal is to keep the precious heat inside your cozy home. But in scorching southern summers, it’s all about keeping that relentless heat outside your air-conditioned sanctuary.

In both scenarios, using argon gas makes sense because it’s denser and heavier than air, which means it’s not as great at conducting heat.
Now, how well your double-pane window works boils down to two things: the insulating power of the glass’s center (we call that the COG) and the frame, along with its spacer. Over time, we’ve gotten smarter about this and have moved from using super-conductive aluminum spacers to what we call “warm-edge” foam spacers. They make a big difference in how well your window keeps you comfy.
Convective heat
Now, let’s talk about convective heat – the last way heat moves through windows.
When a fluid, like air, gets warm, it expands, gets lighter, and rises. This creates a flow of fluid, which we call convection. It’s one of the main ways heat travels through windows. You can see it happening between the air and the glass on both the inside and outside surfaces and even between the panes in double-glazed windows.
To slow down this convection, we fill double-glazed windows with a denser, less mobile gas like argon. While argon is the most common choice, there are even heavier gases like krypton and xenon that work even better, but they come at a higher cost.
Note, in the diagram below, how argon convects at a slower rate than air and therefore transfers less heat.

In summary, conduction and convection act together to transfer heat energy from the high to the low-temperature side. Argon works to slow down both conduction and convection.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases
Benefits of Argon-Filled Windows
Argon gas-filled windows have become increasingly popular due to their numerous benefits. Here are some of the benefits of argon-filled windows:
Thermal Insulation

Argon gas-filled windows provide better thermal insulation than windows filled with air. The insulative properties of the argon gas result in minimum heat exchange through the window. This makes argon windows a good choice for both hot and cold climates. The use of argon gas in windows can also reduce the amount of condensation and frost that forms on windows.

Condensation and Frost Prevention
Argon gas-filled windows can help prevent condensation and frost from forming on windows. This is because the argon gas helps to maintain a consistent temperature on the glass surface, which reduces the likelihood of moisture buildup. This is especially important in colder climates where condensation and frost can be a problem.

Soundproofing
Argon gas-filled windows can also help to reduce noise transmission. The density of the argon gas helps to absorb sound waves, which can result in a quieter indoor environment. This is especially important for those who live in noisy areas or near busy roads.

In conclusion, argon-filled windows offer numerous benefits, including energy efficiency, thermal insulation, condensation and frost prevention, and soundproofing.
Comparing Argon with Other Gases
Argon vs. Krypton and Xenon
Krypton gas is denser than argon, making it a better insulator. However, it is also more expensive than argon. Krypton is typically used in triple-pane windows where the gap between the panes is smaller.
In terms of thermal performance, krypton can improve the U-factor of a Low-E insulating glass unit by up to 27 percent. This is a significant improvement but not as much as some may claim. The cost of krypton gas may not be worth the marginal improvement in performance, especially in double-pane windows where the gap is larger.
Cost and Lifespan Considerations
When considering whether to invest in argon-filled double-pane windows, cost and lifespan are important factors to consider. While the initial cost of these windows may be higher than their non-argon-filled counterparts, they can provide significant cost savings over time.
One of the main benefits of argon-filled windows is their energy efficiency. By reducing heat transfer through the window, they can help to lower energy costs and improve the overall energy efficiency of a home or building. According to Energy Star, upgrading to double-pane windows can result in up to 12% in energy savings per year. However, it’s important to note that the exact amount of savings will depend on a variety of factors, including climate, window orientation, and building design.
Save money by installing your own windows
A major part of the cost of replacement windows is the cost of labor. Handy homeowners can save big bucks by installing their own windows.
Purchase double-pane windows from your local glass company, big box store, or even online.
Custom, cut-to-size Insulated glass with Low-E (Pilkington) and with argon gas filling – is available from vendors like this on Amazon. Compare costs with local big-box stores.
FAQs
- What is a noble gas?
- What are the properties of argon?
- How are double paned windows filled with Argon?
- Can argon be added to existing double-pane windows?
- How long does argon last in double-pane windows?
- Can argon improve the sound insulation of double-pane windows?
- Is argon safe to use in double-pane windows?
- Is argon “environmentally friendly”?
- How should I maintain my argon-filled double-pane windows?
- How does argon compare to krypton & xenon, for filling double-pane windows?
- Does argon affect the appearance or clarity of double-pane windows?
- Are argon-filled windows easy to clean?
- Are argon-filled double-pane windows more expensive than regular windows?
- How is argon gas separated from air?
- What regulations control the production of Argon-filled windows?
What is a noble gas?
A “noble gas” (inert gas) is a gaseous chemical element that does not readily enter into chemical combination with other elements. Noble gases are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity.

What are the properties of Argon?
Argon makes up 0.94% of the Earth’s atmosphere and is the third most abundant atmospheric gas. Levels have gradually increased since the Earth was formed because radioactive potassium-40 turns into argon as it decays. Argon is obtained commercially by the distillation of liquid air.
Although argon is non-toxic, it is 38% more dense than air and therefore considered a dangerous asphyxiant in closed areas. It is difficult to detect because it is colorless, odorless, and tasteless.
The thermal conductivity of argon at room temperature (300 K) is 17.72 mW m-1K-1 (milliWatts per meter per degree) – much lower than air (26 mW m-1K-1 )
How are double-paned windows filled with Argon?
Argon gas is pumped into the space between the double panes to achieve the industry-standard minimum of 90% argon gas.
To hit that target, manufacturers use specialized equipment -as the argon goes in, it pushes the regular air out, and that air is vented away from the IGU. Oxygen analyzers keep a close watch on this process to make sure there’s enough argon and not too much air.

Sealing the Windows
Now, once they’ve got the right amount of argon in there, they’ve got to seal things up tight to keep that precious gas from escaping. Manufacturers use different sealing materials like silicone, polyisobutylene, and hot-melt butyl. They spread these sealants along the edges of the glass panes and the spacer. After that, they press the panes together to make a super snug seal. Then, the sealant gets cured to create a strong bond. That’s how they keep the argon where it belongs and make your windows nice and efficient.
Can argon be added to existing double-pane windows?
No – it’s not practical or cost-effective to add argon gas to existing double-pane windows. This is because argon gas is injected into the insulating space between the panes during the manufacturing process. Retrofitting existing windows would require a complex and expensive process of removing the sealed glass units, injecting argon, and resealing the units. Furthermore, there is a risk of damaging the window frames during this process. If you’re looking to improve the energy efficiency of your windows, it’s more sensible to consider replacement windows that come pre-filled with argon gas or explore other energy-saving solutions like weatherstripping or adding window films.
How long does argon last in double-pane windows?
When properly sealed, argon gas can last for the entire lifespan of the window, which is typically 20-25 years or more. While it’s true that some argon gas may gradually dissipate over time, the rate of loss is typically quite slow (commonly estimated at about 1% each year). This means that after several decades, there may be a noticeable decrease in the gas’s insulating effectiveness. However, it’s essential to note that even with some argon loss, double-pane windows can still provide energy-saving benefits for many years.
Properly sealed and maintained double-pane windows can continue to offer improved insulation and energy efficiency well beyond their initial installation. To maximize their lifespan and performance, it’s crucial to have your windows professionally installed and periodically inspected for any signs of seal failure or gas leakage.
Can argon improve the sound insulation of double-pane windows?
Argon gas is primarily used to enhance the energy efficiency of double-pane windows by reducing heat transfer. However, it also has a positive impact on sound insulation. The denser nature of argon gas compared to air reduces sound transmission through the glass. This means that windows filled with argon gas provide a quieter indoor environment by blocking out external noise. However, it’s important to note that the degree of sound insulation improvement will depend on various factors such as the thickness of the glass, the quality of the seal, and the frequency of the sound. Also, while argon gas can help reduce noise, it’s not a complete soundproofing solution. Other measures such as acoustic curtains or double-glazed windows with laminated glass are necessary for optimal noise reduction.
Is argon safe to use in double-pane windows?
Yes, argon gas is safe to use in double-pane windows. Argon is a colorless, odorless, non-toxic, and non-reactive inert gas. Although minor leaking (about 1% per year) can be expected, this poses no health risks or safety concerns to occupants of the building.
Is Argon “environmentally friendly”?
Argon is a naturally occurring gas and third-most abundant in Earth’s atmosphere, at 0.934%. Extracting and using argon for window insulation does not deplete or harm the environment. Furthermore, argon-filled double-pane windows contribute to energy efficiency, reducing the need for heating or cooling, which in turn helps lower energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, making them an environmentally responsible choice for improving the energy efficiency of buildings.
How should I maintain my argon-filled double-pane windows?
Double-pane windows filled with argon gas require minimal maintenance. However, some general practices can help ensure they continue to perform optimally over their lifespan:
- Regular Cleaning: Cleaning the windows regularly helps maintain their appearance and clarity. Use a mild glass cleaner and a soft cloth to avoid scratching the glass or damaging the window seals.
- Seal Inspection: Periodically inspect the window seals for any signs of damage, cracking, or deterioration. Damaged seals can lead to gas leakage and reduced insulation properties. If you notice any issues, it’s advisable to consult a professional for repairs.
- Condensation Management: Condensation between the panes can be a sign of seal failure or gas leakage. If you observe condensation inside the windows, it’s important to address it promptly to prevent further damage. This often involves replacing the affected window unit.
- Frame Maintenance: Ensure that the window frames and hardware are in good condition. Check for any signs of wear, rust, or damage and address any issues as needed.
- Weatherstripping: Maintain the weatherstripping around the window frames to prevent drafts and maintain energy efficiency. Replace any worn or damaged weatherstripping.
- Professional Inspection: Consider having a professional window technician inspect your double-pane windows every few years to identify any potential issues and ensure they are functioning as intended.
In general, well-maintained double-pane windows with argon gas fill should provide energy efficiency and insulation benefits for many years. Regular upkeep can help extend their lifespan and preserve their performance.
How does argon compare to krypton & xenon for filling double-pane windows?

Argon Gas:
- Performance: Argon is the most commonly used insulating gas in double-pane windows. It is an inexpensive, non-toxic, and non-reactive gas that provides decent thermal insulation. It can significantly reduce heat transfer between the panes of glass, which improves the window’s overall energy efficiency.
- Cost: Argon is relatively inexpensive compared to krypton and xenon. This makes it a cost-effective choice for most residential and commercial applications.
Krypton Gas:
- Performance: Krypton is denser than argon, which means it offers better thermal performance. It provides superior insulation, especially in thinner gaps between the glass panes. Krypton-filled windows typically have lower U-values than argon-filled ones.
- Cost: Krypton is more expensive than argon. Due to its higher cost, it is often used in specialty applications where maximum thermal efficiency is required, such as in some high-end residential windows.
Xenon Gas:
- Performance: Xenon is even denser than krypton and offers the highest level of thermal insulation among the three gases. It can be a suitable choice for extremely energy-efficient windows, especially those designed for passive house construction or other high-performance building standards.
- Cost: Xenon is the most expensive of the three gases, and its use is relatively rare in standard residential and commercial windows. It is mainly reserved for specialized projects with a focus on energy efficiency.
In summary: argon is a cost-effective and widely used option that provides good insulation. Krypton and xenon offer superior thermal performance but come at a higher cost, making them suitable for projects where maximum energy efficiency is a priority. It’s essential to consider your project’s requirements and budget when selecting the appropriate gas fill for your double-pane windows. Additionally, always check the latest market trends and pricing, as they may fluctuate over time.
Does argon affect the appearance or clarity of double-pane windows?
Argon gas is colorless, odorless, and non-toxic. It does not have any properties that affect the clarity or appearance of the windows. When you look through double-pane windows filled with argon gas, you will see the same level of clarity as you would with regular air-filled double-pane windows.
Any issues related to clarity or appearance are more likely to be associated with factors such as the quality of the window manufacturing, installation, or maintenance rather than the presence of argon gas itself.
Are argon-filled windows easy to clean?
Cleaning argon-filled windows is no different from cleaning regular windows. You can use standard glass cleaning products and techniques. The argon gas remains sealed inside, so cleaning won’t affect its insulating properties.

Are argon-filled double-pane windows more expensive than regular windows?
While argon-filled windows may have a slightly higher upfront cost, the long-term energy savings they provide often outweigh the initial investment. These days, Argon-fill is pretty much standard in double-pane units so most consumers will not be able to find air-filled units.
Remember that in addition to energy savings, argon-filled windows can increase the value of your home.
How is argon gas separated from air?
Argon constitutes almost 1% of the earth’s atmosphere. Extracting argon gas from air is a technically complex process, but it is not necessarily difficult for industrial facilities equipped with the necessary equipment and expertise.
Argon is separated as a by-product of the extraction of oxygen – a process, known as cryogenic air separation. This involves cooling and distilling air to separate its various components, including argon, nitrogen, and oxygen, based on their different boiling points.
What regulations control the production of Argon-filled windows?
Energy Star, a program run by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) that sets standards for energy-efficient products. Energy Star has established criteria for windows that include specific requirements for U-factor, solar heat gain coefficient (SHGC), and visible light transmittance (VT). In order to be Energy Star certified, windows must meet these criteria and be independently tested and certified by the National Fenestration Rating Council (NFRC).
The NFRC is a non-profit organization that develops and administers energy performance ratings for windows, doors, and skylights. The NFRC rating system includes the U-factor, which measures the rate of heat transfer through a window, and the SHGC, which measures the amount of solar heat that passes through a window. The lower the U-factor and SHGC, the more energy-efficient the window.
To fullyunderstand the meaning of the EnergyStar labels – jump to this comprehensive post by Artistry in Glass.
In addition to Energy Star and NFRC, there are also industry standards for the manufacture and installation of argon-filled double-pane glass. These standards include ASTM E2190, which specifies the performance requirements for insulating glass units, and ASTM E2188, which specifies the laboratory testing procedures for insulating glass units.
Overall, following these regulations and standards is crucial for ensuring the quality and energy efficiency of argon-filled double-pane glass. By meeting these criteria and undergoing independent testing and certification, consumers can have confidence in their purchase and enjoy the benefits of improved thermal performance and energy savings.
Learn all about energy-efficient windows in these posts:
- What is Low-E Glass & how can it reduce your utility bills?
- How do argon-filled windows save on energy bills?
- Are replacement windows worth the investment?
- Understanding the Labels on Your Double-Pane Glass Windows
- Is Upgrading to Triple-Pane Windows Cost-Effective?
- The Ultimate Window Frame Material Challenge – which is best?



